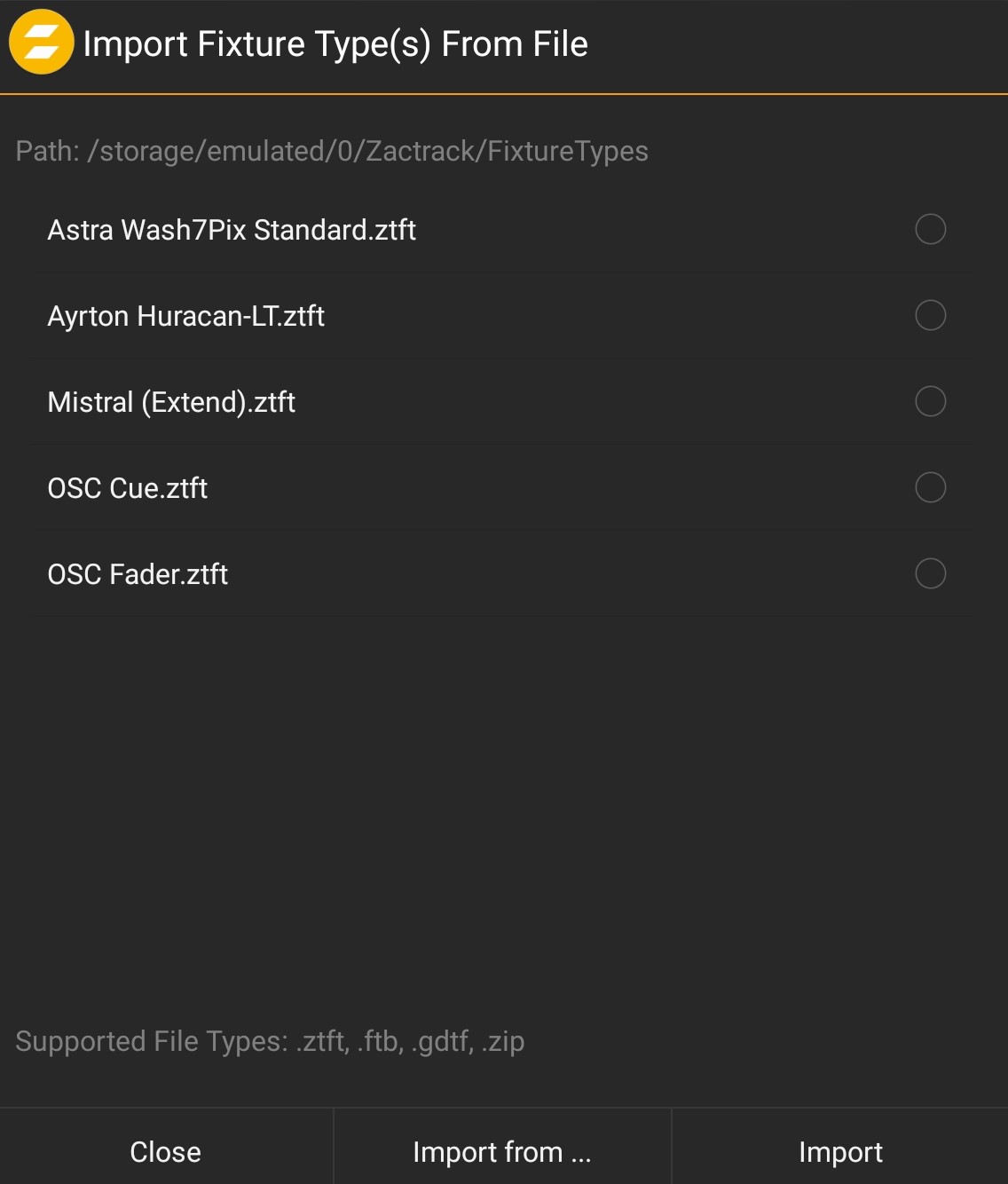
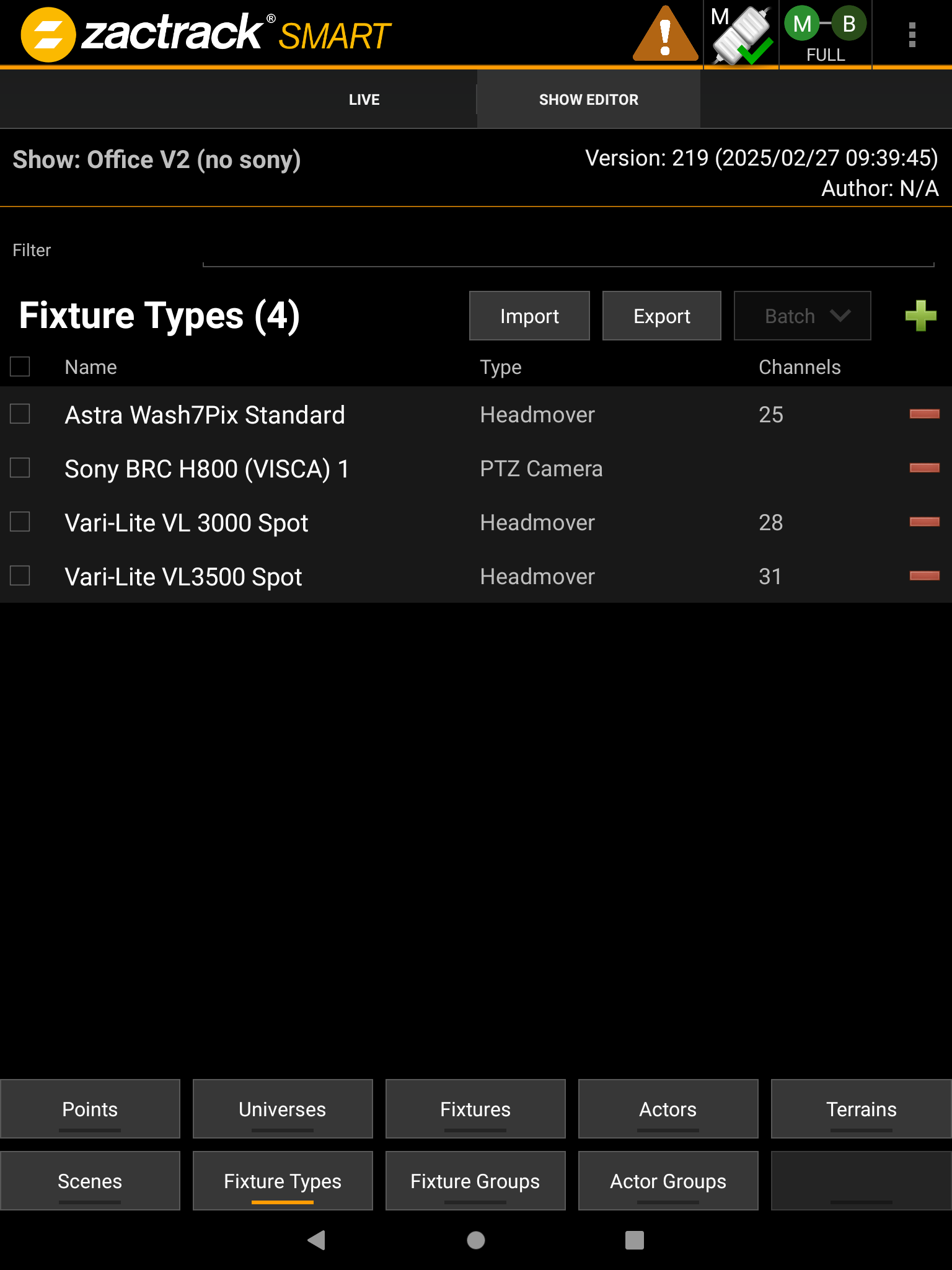
Fixture Types
To use Fixtures in the zactrack App it is necessary to import a Fixture Type first.
 |
Batch Edit
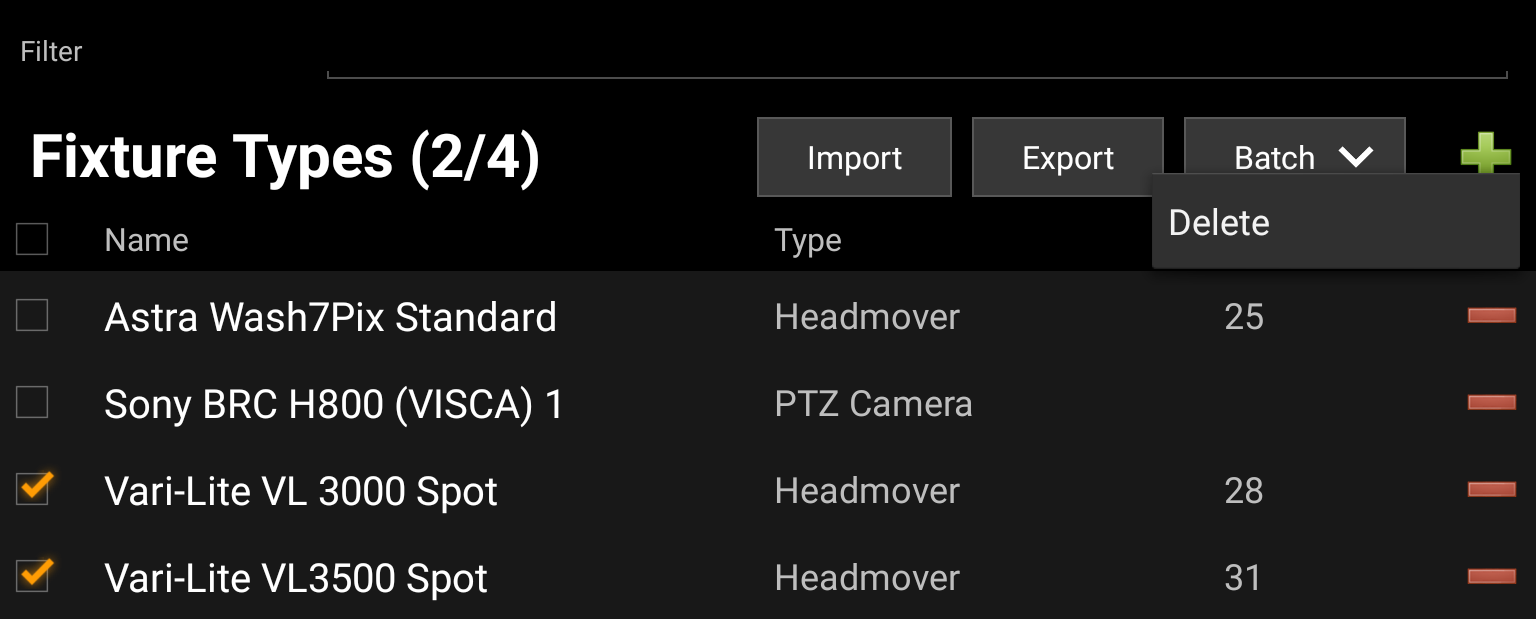 |
Multiple Fixture Types can be deleted at once when selecting the respective items' checkboxes and pressing Batch and select Delete.
Press the  icon to add a Fixture Type.
icon to add a Fixture Type.
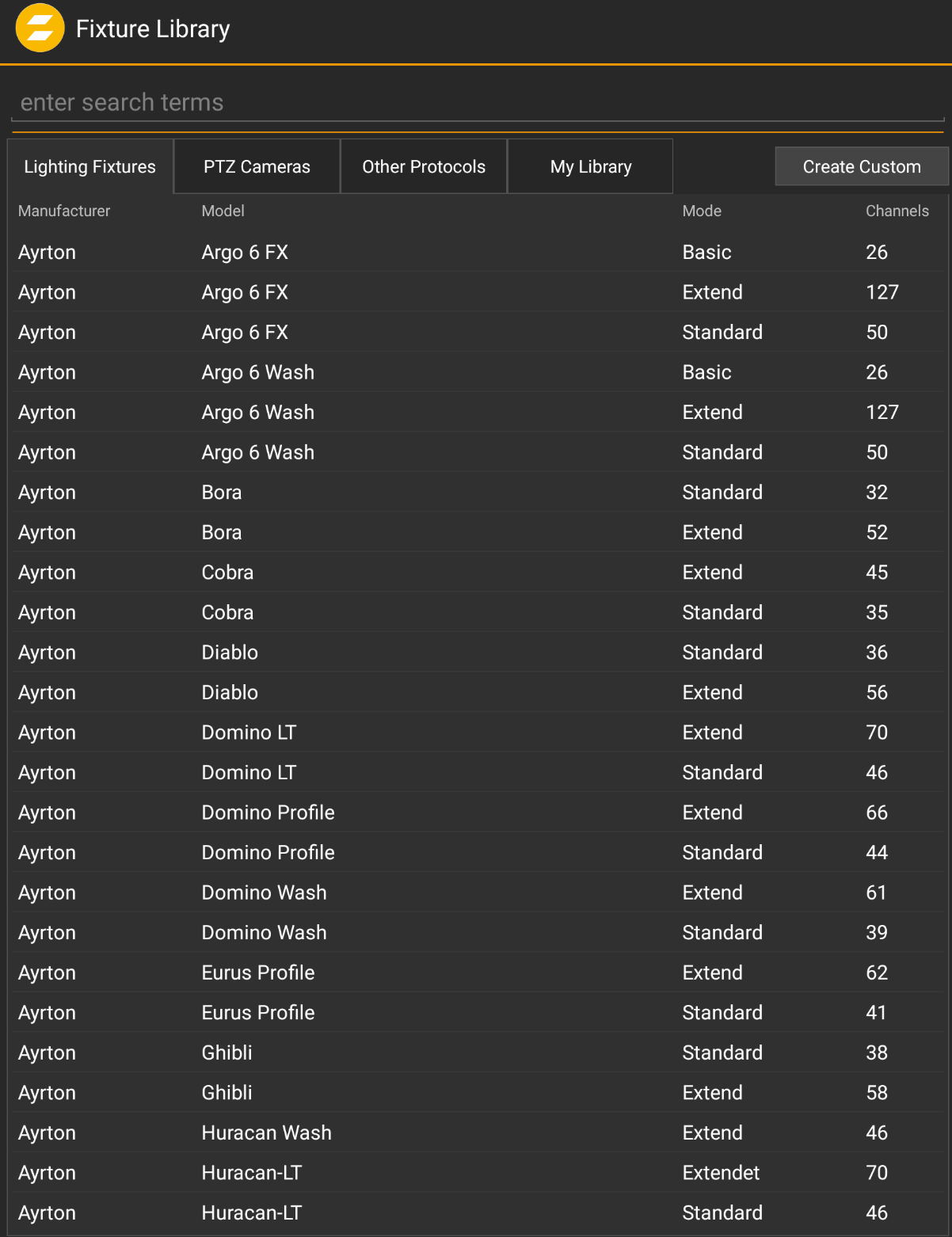 |
The zactrack App includes a lot of different Fixture Types in the Lighting Fixtures Library. It is possible to create your own Fixture Type or change settings of an existing Type.
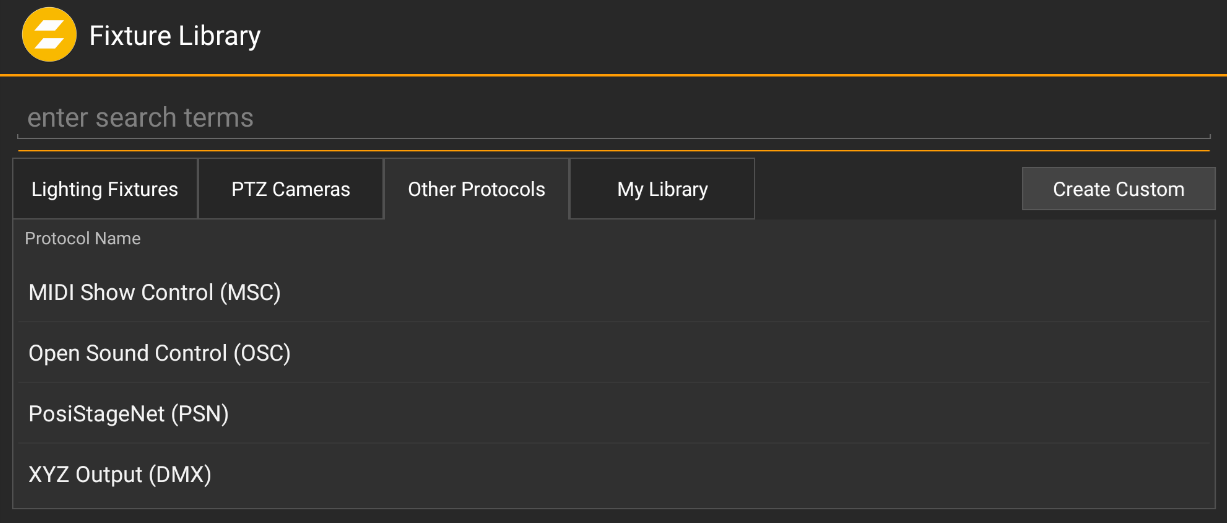 |
In the next tab under Other Protocols there are more Fixtures independent of lighting.
MIDI Show Control (MSC)
Create custom MSC Fixture Types. See MIDI Show Control for more information.
Open Sound Control (OSC)
Create custom OSC Fixture Types or chosse one out of the Library. See Open Sound Control for more information.
PosiStageNet (PSN)
Create custom PSN Fixture Types. See Posi Stage Net for more information.
XYZ Output (DMX)
Create custom XYZ Fixture Types with DMX output. See the section Create a XYZ Output Fixture Type below.
In the Fixture Type Dialog a Create Custom button can be found.
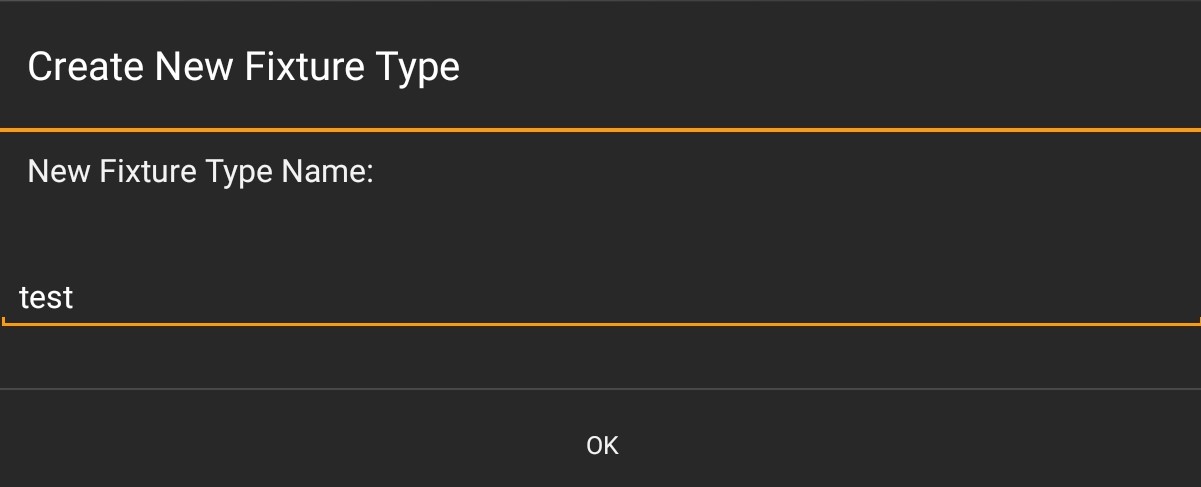
Add a name for the Fixture Type.
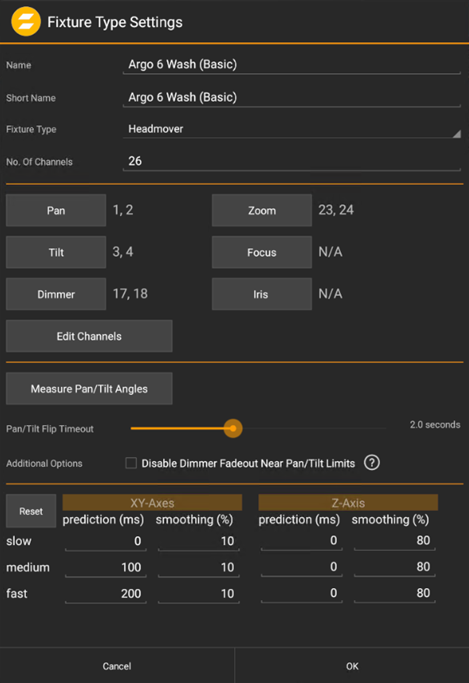
Create/edit the Channelset for the Fixture Type by clicking the Pan/Tilt/Dimmer/... buttons or Edit Channels. This opens the Channel Function Dialog. More information is listed below.
The Fixture Type has multiple parameters to be set:
Name / Short Name
Name of the Fixture Type.
Fixture Type
Choose from:
Headmover
Standard Moving Head.
Mirror
Mirror based Fixture e.g. Scanner
No.of Channels
Total number of channels for the Type. Necessary to patch correctly.
Pan / TIlt / Dimmer / Zomm / Focus / Iris
This 6 channels are modified within the zactrack system if AUTO 6 is used.
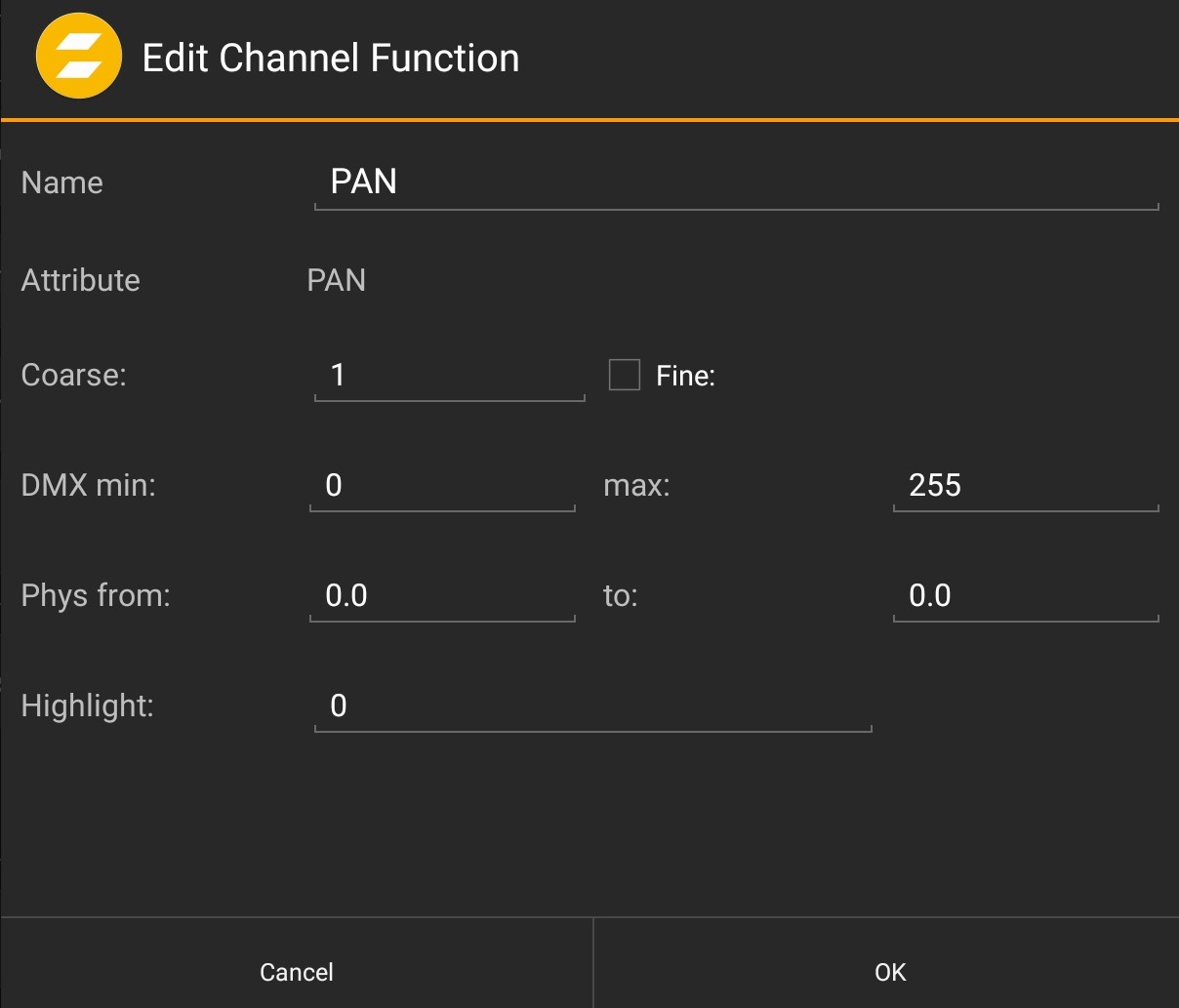
Edit Channels
To be able to use the highlight function, a usage without the console, zactrack needs at least all channels to set an output.
Shutter, RGB, ...
Measure Pan/Tilt Angles
zactrack uses the physical limits of a channel to calculate the position of the Fixture in the Fixture Alignment. If these values are not available it is possible to measure them. Often some of the older fixtures have no correct values. It is possible to measure these values in the Fixture Type, or directly in the Fixture window. See Fixture for more information.
Pan/Tilt Flip Timeout
Turns off the dimmer for a predefined period if a pan or tilt flip is detected. The timing needs to be adjusted depending on how much time the fixture needs to perform the pan/tilt flip.
Disable Dimmer Fadeout Near Pan/Tilt Limits
When enabled, fixtures of this type will not dim out near its pan/tilt movement limits, regardless of the global settings. Useful for fixtures with continuous or infinite movement where edge dimming is not desired.
Note
For basic Control (Auto 2) zactrack needs at least PAN and TILT channel information.
Warning
Attention to the physical range of the channels. They are important for the correct function.
In the Fixture Library Dialog switch to the PTZ Cameras tab.
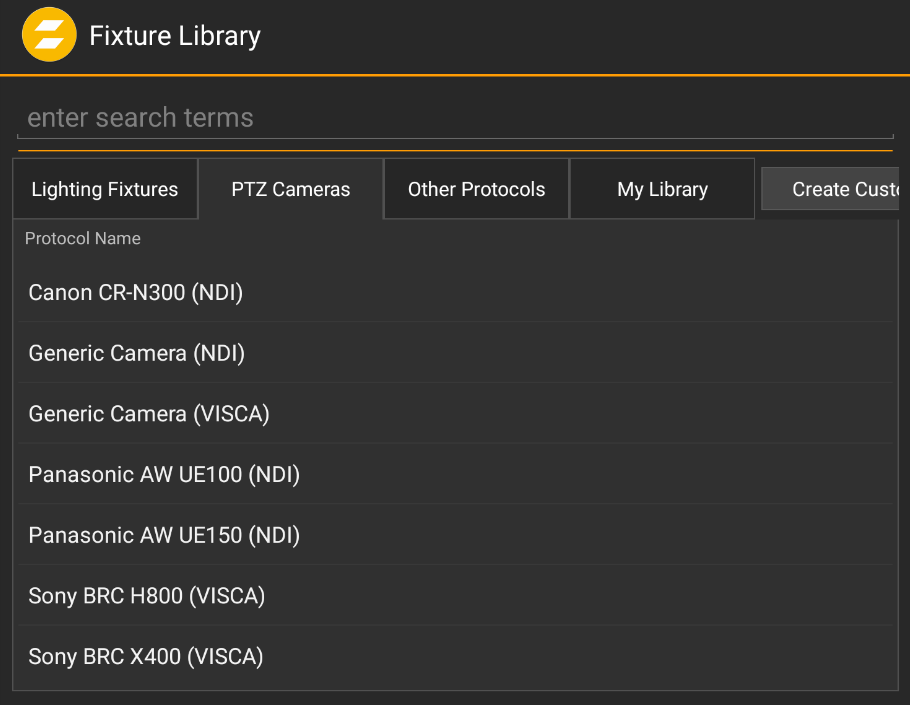
Select a supported camera model or a generic type.
Add a name for the Fixture Type.
Define details and settings for the PTZ camera Fixture Type.
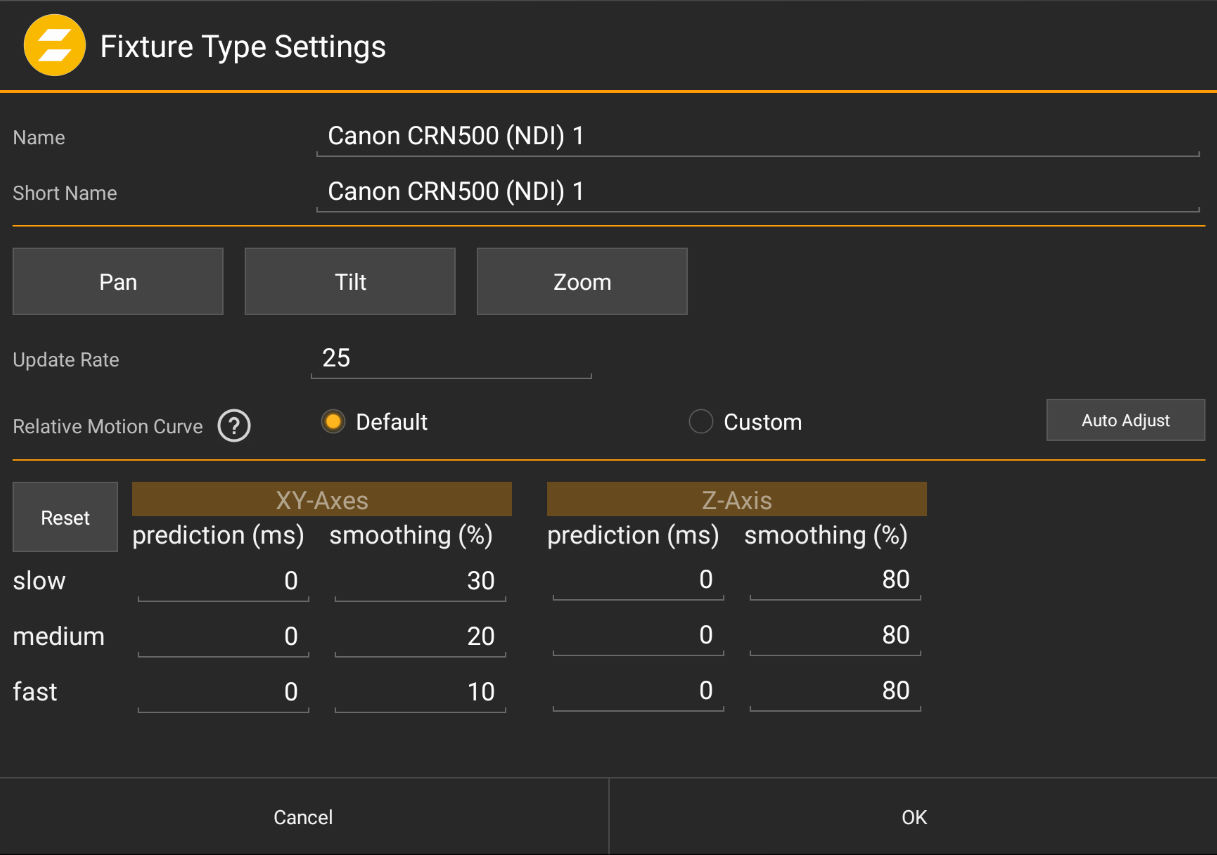
The PTZ Fixture Type has multiple parameters to be set:
Name / Short Name
Name of the Fixture Type.
Edit Channels
Allows you to edit the channels for pan/tilt/zoom in case of a differently configured PTZ cameras. It is recommended to keep these settings unchanged.
Update Rate
Define the update rate for the camera control protocol.
Relative Motion Curve
Define the details of the speed curve for controlling the camera's pan/tilt motors. In case of specific camera models (i.e. non-generic), "Default" is the recommended option. For generic camera models, the speed curve settings can be adjusted using the "Custom" option. Tapping the help icon shows an explanation of the individual parameters.
Tapping the "Auto Adjust" button brings up the PTZ Camera Setup Wizard, which helps to automatically determine motion curve parameters. This requires at least one Fixture instance of the PTZ Fixture Type to be present and configured in the show.
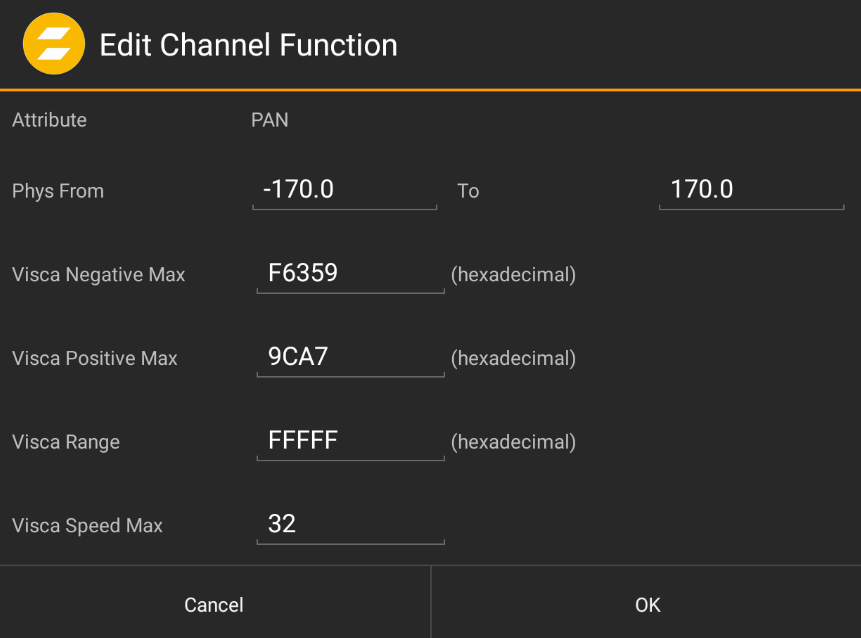
Depending on the control protocol (NDI or VISCA), Pan/Tilt/Zoom controls need different parameters. In case of specific camera models (i.e. non-generic), these settings are already pre-defined and usually need no adjustment. For generic models, these values need to be checked with the camera manufacturer, i.e. the model's technical documentation.
Channel parameters for NDI-based controls
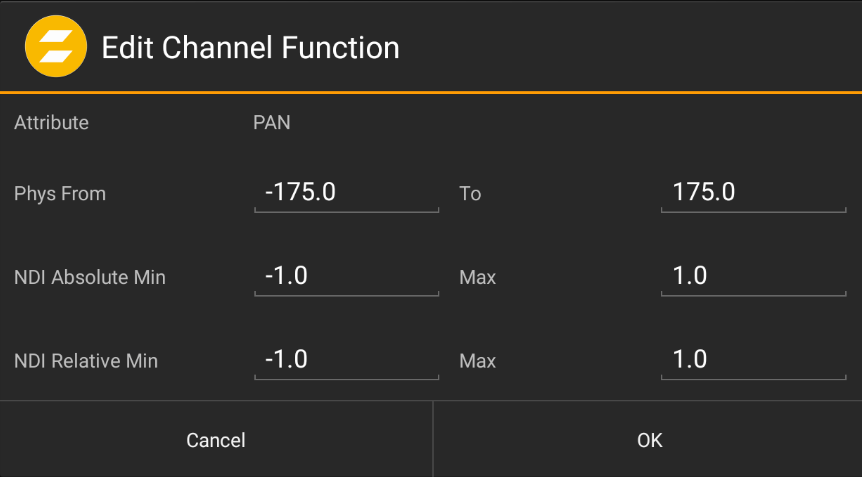
Channel parameters for VISCA-based controls
This Fixture Type generated PSN datafor a given set of axes, allowing the conversion of positional data into DMX ranges for one or multiple axes.
In the Fixture Type Dialog switch to the Other Protocols tab.
Select PosiStageNet (PSN).
Add a name for your Fixture Type.
Define details and settings for the PSN Output Fixture Type.
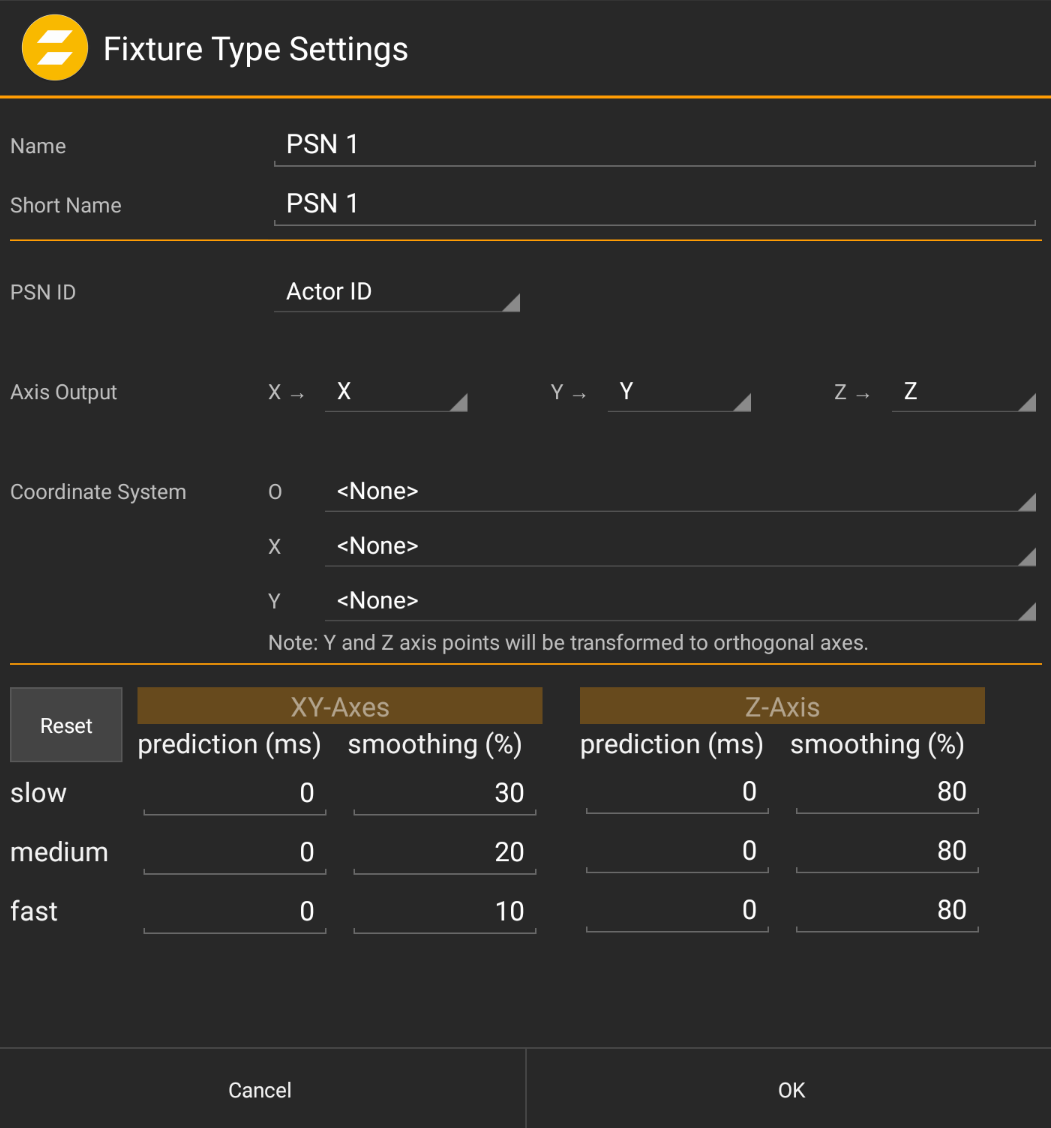
The PSN Output Fixture Type has multiple parameters to be set:#
Name / Short Name
Name of the Fixture Type.
PSN ID
Which ID shall be used for the data packet: Options are Fixture ID or ID of the currently assigned Actor.
Axis Output
Define which axes shall be contained in which order. Axes can be inverted, too.
Coordinate System
Definition of the coordinate system to which the output shall relate. Similar to the tracking system calibration, the Y and Z axis points will be transformed to orthogonal axes.
Note
These settings are replacing the cp.80/81/... point definitions used in previous software versions.
This Fixture Type generated DMX values for a given set of axes, allowing the conversion of positional data into DMX ranges for one or multiple axes.
In the Fixture Type Dialog switch to the Other Protocols tab.
Select XYZ Output.
Add a name for your Fixture Type.
Define details and settings for the XYZ Output Fixture Type.
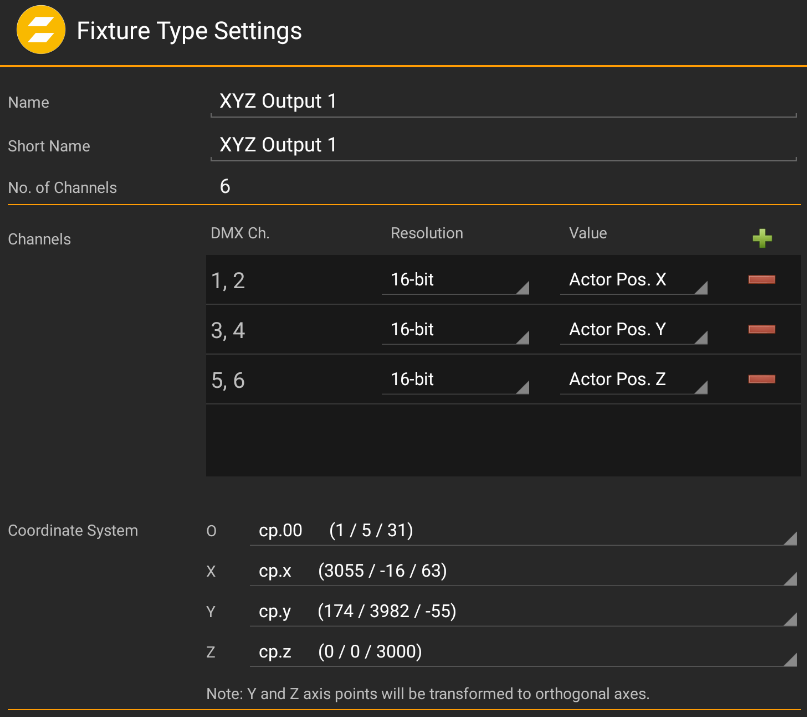
Click the
 button to add more channel outputs.
button to add more channel outputs.Each channel output can be defined in both 8-bit and 16-bit resolution and contain either a specific axis coordinate or the Actor's DMX ID.
Select up to 4 Calibration Points to define the coordinate system upon which the output shall be computed. The X/Y/Z points define both the axis orientation as well as the range endpoint for that particular axis.
In the Fixture Type Settings it is possible to change channel sets, physical ranges, speed settings, ...
 |
 |
In the Edit Channels window, all channels with their highlight value can be found.
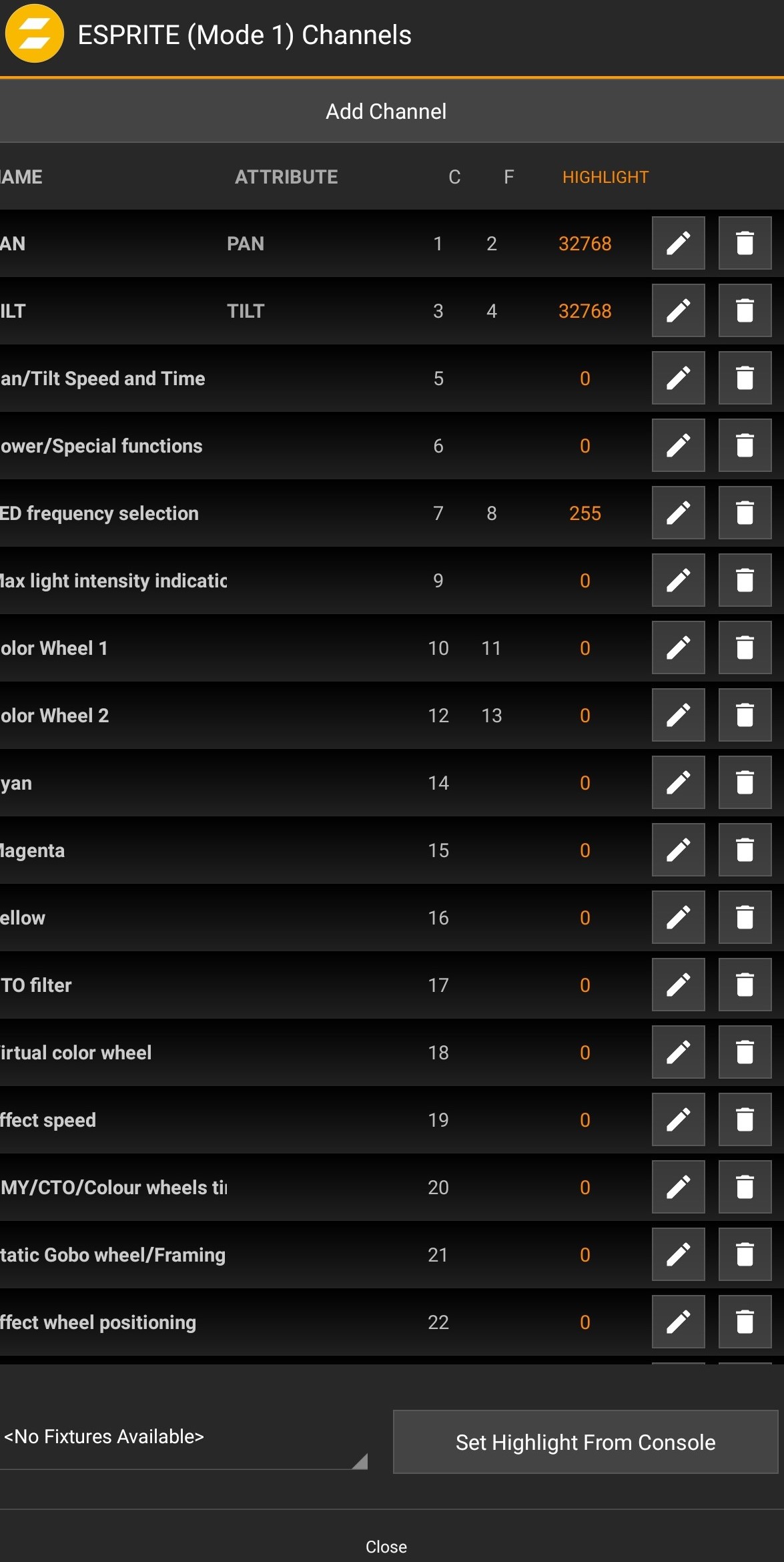 |
It is possible to add a channel. E.g. for highlight values.
Speed Settings:
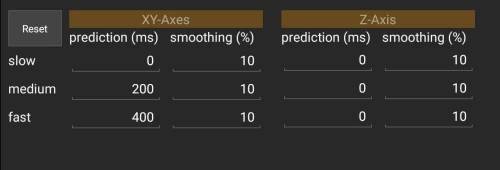 |
Every Fixture Type has a prediction and a smoothing value. It is split in XY and Z Axis.
Note
It`s possible to change the setting Slow, Medium, Fast in the live view or over the console.
Tip
Prepare the values for your show situation and change the preset live in your show.
Prediction
Due to the mass of a Fixture and a System Delay it is necessary to predict the Fixture into to the Future.
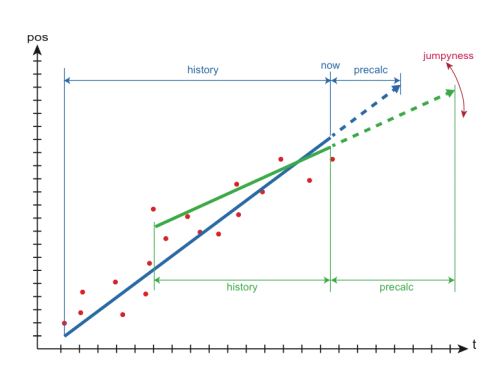
XYZ positions in the past are used to predict the future position
Precalc time pushes the position further into the future
Higher precalc makes the curve “jumpy
0-1000ms common precalc range
Warning
A high value, will push the light or the position more in the future. In case of a stop it will overswing.
Smoothing
During the movement Smoothing will filter the signal.
Length of history defines the smoothness of the curve
Short history makes the curve less smooth
Long history adds up more latency
0% → no smoothing → almost raw signal
10% - 100% common smoothing range
Use the Export button.
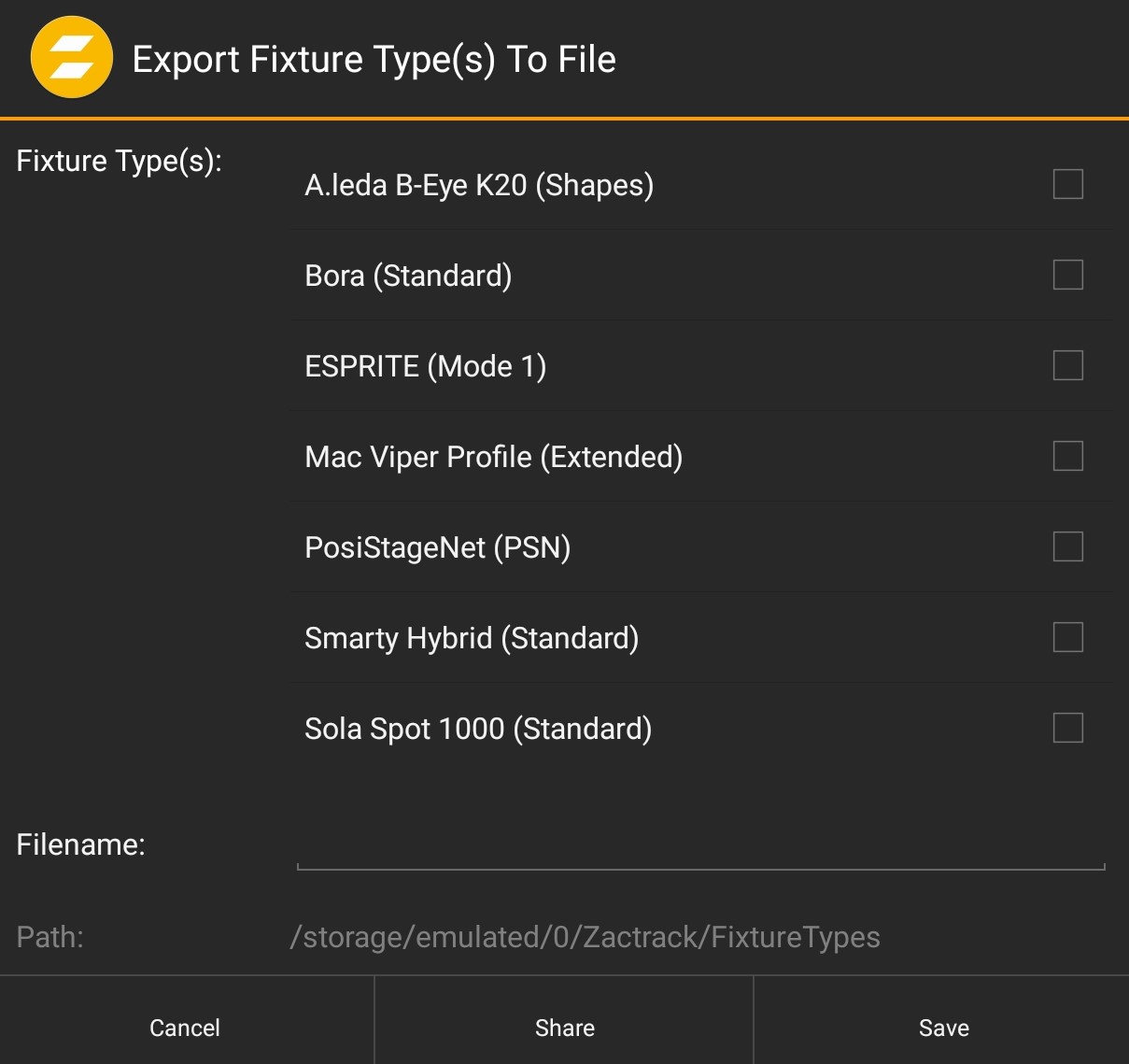 |
Use this function to export zactrack native files to the tablet file system.